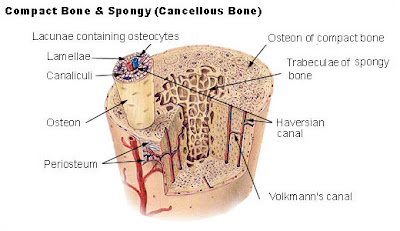
The sternum is composed of highly vascular cancellous tissue, covered by a thin layer of compact bone which is thickest in the manubrium between the articular facets for the clavicles.
The sternum is composed of highly vascular cancellous tissue, covered by a thin layer of compact bone which is thickest in the manubrium between the articular facets for the clavicles. The sternum is an elongated, flattened bone, forming the middle portion of the anterior wall of the thorax. Its upper end supports the clavicles, and its margins articulate with the cartilages of the first seven pairs of ribs. It consists of three parts, named from above downward, the manubrium, the body or gladiolus, and the xiphoid process; in early life the body consists of four segments or sternebrœ. In its natural position the inclination of the bone is oblique from above, downward and forward. It is slightly convex in front and concave behind; broad above, becoming narrowed at the point where the manubrium joins the body, after which it again widens a little to below the middle of the body, and then narrows to its lower extremity. Its average length in the adult is about 17 cm., and is rather greater in the male than in the female.
Surfaces.—Its anterior surface, convex from side to side, concave from above downward, is smooth, and affords attachment on either side to the sternal origins of the Pectoralis major and Sternocleidomastoideus. Sometimes the ridges limiting the attachments of these muscles are very distinct. Its posterior surface, concave and smooth, affords attachment on either side to the Sternohyoideus and Sternothyreoideus.